Bloom Filter
introduction
首先,我们假设有四种存储设备,分别是 Tape, HDD, SSD, Memory.当然,我们知道,这四种设备的响应速度是按顺序递增的,也就是说 Memory 的速度最快,当然,我们都希望所有的程序都可以跑在 Memory 中,但是这四种设备的存储大小即容量也是不一样的,价格也是随之递增的.Ex .g 当我们在 Java 中使用 Set 类型去存储数据的时候,数据越多,查询所需的时间越长,同时 Jvm heap 也越大.实际生产环境中的数据量极大,在一些实时性要求比较高的应用当中,不可能将所有的数据都放在 Memory 中,当允许一定的误差的情况下,(即使用准确性去换取实时性,这是一种 tradeoff)这里就提出了,一种 Probabilistic data structure,它可以在一定程度上去接受一定的误差,从而使响应速度加快,所要存储的数据也大大缩小.
Bloom Filter 的概念提出的比较早,早在1970年就由一个叫 Bloom(真的叫这个名字)的人在一篇名为"Space / Time trade-offs in hash coding with allowable errors"
structure
Initial the structure

Add an element to this structure
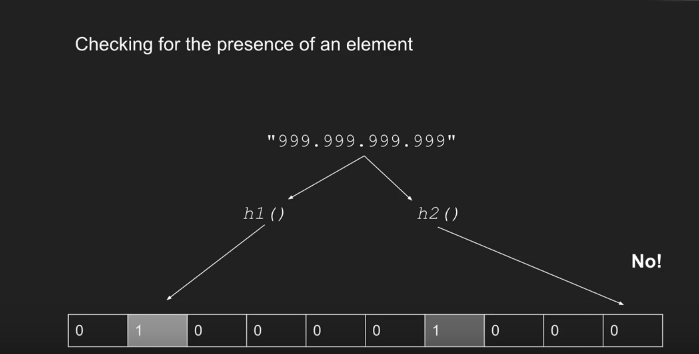
query 判断存在还是不存在
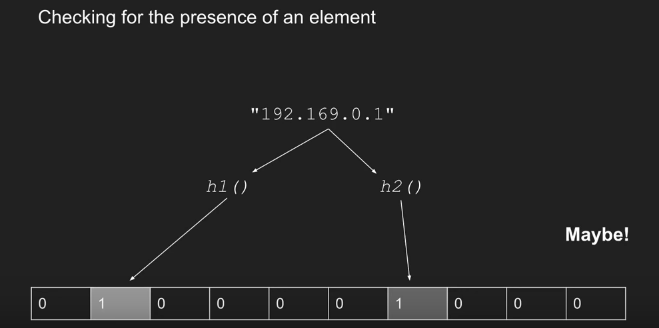
If one hash function map to 0, It means NO!( 有一个 map 到0 就不行) But if all hash functions map to 1, it means maybe YES(即使 所有的 hash 函数都能 map 到1, 也不能说明就一定存在, 这里有一定的 false positive, 即认为是正确的,但实际上不是正确的概率)
use cases
- one hit wonders
- avoiding lookups
- real-time matching
Count-Min Sketch
introduction
Count-min Sketch 是一个概率数据结构,用作数据流中事件的频率表。它使用散列函数将事件映射到频率,但与散列表不同,散列表仅使用子线性空间,但会因过多计算冲突导致的某些事件。
Count-min Sketch 本质上与 Fan 等人在 1998 年引入的计数 Bloom filter 相同的数据结构. 但是,它们的使用方式各不相同,因此尺寸也有所不同:计数最小草图通常具有次线性单元数,与草图的所需近似质量有关,而计数 Bloom filter 的大小通常与其中的元素数集合。
Main aim is to count things, how many times have i seen an element
structure
实际的草图数据结构是 w 列和 d 行的二维数组。参数 w 和 d 在创建草图时是固定的,并确定时间和空间需求以及在查询频率或内部产品草图时的错误概率。与每个 d 行相关联的是一个单独的散列函数; 哈希函数必须是成对独立的。参数 w 和 d 可以通过设置 w =⌈e/ε⌉和 d =⌈ln1 /δ⌉来选择,其中在回答查询时的误差在概率为 1 - δ的附加系数ε内(见下文) ,e 是欧拉数。
- 结构图
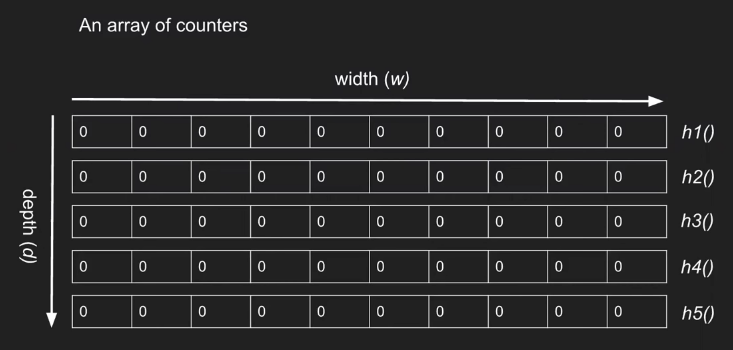 对于 Hash Function 的要求,可以是最简单的 hash function ,但所有的 hash function 必须不同.
对于 Hash Function 的要求,可以是最简单的 hash function ,但所有的 hash function 必须不同.
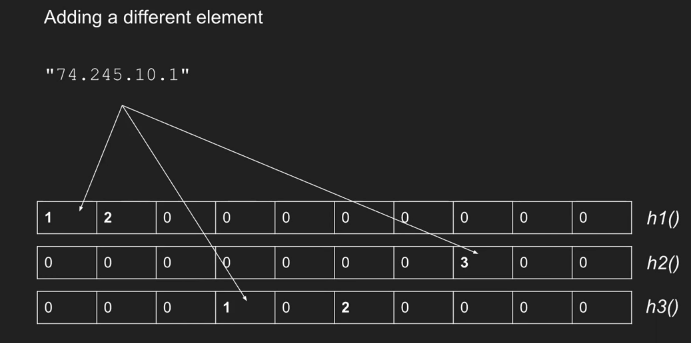
- 添加元素
当一个新的类型 i 事件到达时,我们更新如下:对于表中的每一行 j,应用相应的散列函数来获得列索引 k = hj(i)。然后将第 j 行第 k 列中的值加 1。

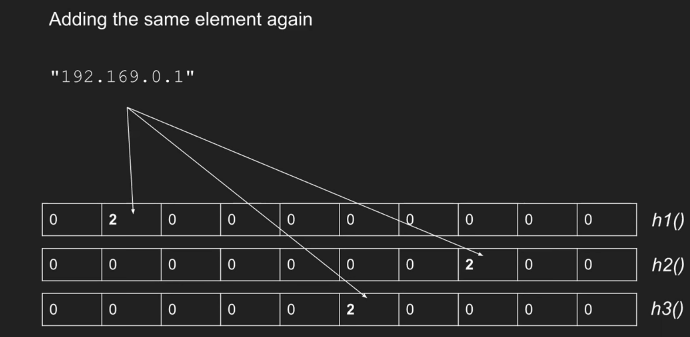
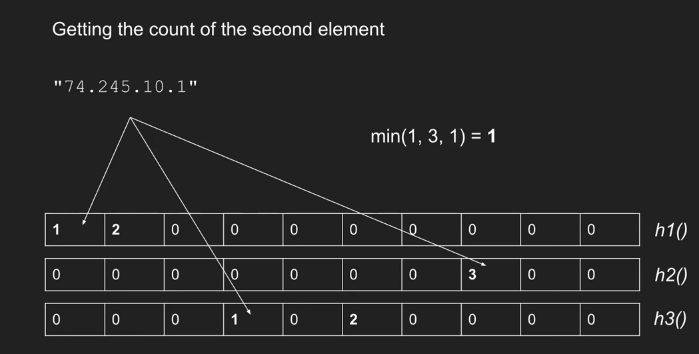
- 查询(统计元素个数)
The estimated count is given by the least value in the table for i, namely {\displaystyle {\hat {a}}{i}=\min {j}\mathrm {count} [j,h{j}(i)]} {\hat a}{i}=\min {j}{\mathrm {count}}[j,h{j}(i)], where {\displaystyle \mathrm {count} } {\mathrm {count}} is the table.
就是取最小的 count 作为 element 出现的次数,故名 count-min

Probabilistic problem
Epsilon: accepted error added to counts with each item Delta: probability that estimate is outside accepted error
use cases
- any kind of frequency tracking
- NLP (word count)
- Extension heavy-hitters
- range-query
参考
James Stanier 的演讲教程 wikipedia 解释 Algorithms & Data Challenges Berlin Meetup Mar 19, 2013 PPT An Improved Data Stream description: The Count-Min Sketch and Its Applications